Construction and HSE team must ensure that hazard identification is complete before start of the drainage piping work.
The construction and HSE team must prioritize the hazard issues, which are of significant in nature. (It means that risks have well established legal requirements, potentially high risks).
Construction and HSE team to prepare the risk assessment plan for the priorities identified hazards for these potential high risks.
Risk is the probability of an event occurring in a given set of circumstances. The ‘event’ is an exposure to hazard. The hazard is the potential to cause harm. The risk assessment is the technique of evaluating not just the likelihood of an event occurring, but also the outcome will be in terms of injury, loss, damage or harm.
Risk Assessment Process
The process of carrying out a risk assessment should be as follows.
Identify the hazards.
Identify who might be harmed and how.
Evaluate the risk and implement the control measures.
Record the significant findings.
Review the assessment and update if necessary.
Examination of the Hazards and Associated Risks
Competent staff must be used in examining the risk associated with the identified hazard.
The competent staff should examine following aspect to determine the risk involved:
Examine the existing control measures in place.
Identify employees at risk.
Likelihood of risk.
Severity of damage or loss
Risk level and their tolerability.
Evaluating the Risk
Once the necessary information has been obtained on the hazards encountered by work activities, next stage is to access the risks.
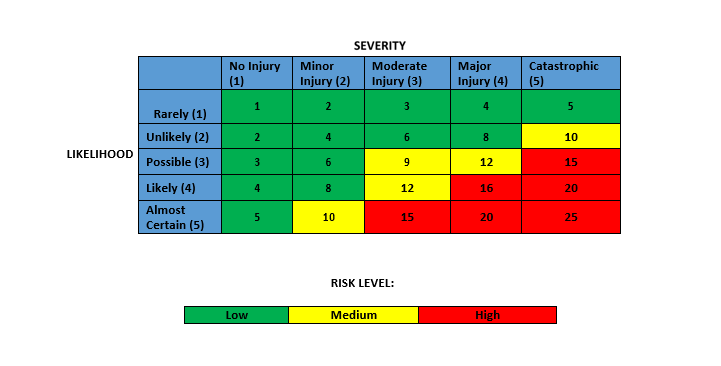
Risk Rating Score
Risk rating score is a combination of two factors.
The severity of the risk that could injure persons or cause damage to plant.
Likelihood of the risk that it could happen (Probability).
RISK RATING = LIKELIHOOD X SEVERITY
NOTE: Each activity has to be assessed for the risk value for determining the level of Severity and likelihood, as mentioned in the table below.
Detailed Risk Assessment for Drainage Works
| ACTIVITY | IDENTIFIED HAZARDS/RISKS | People Involved | Base Risk Ranking (Without Controls) | CONTROL MEASURES | Residual Risk Ranking (With Controls) | Responsible Person | ||||||||||
| L | S | Risk Score | Risk Rating | L | S | Risk Score | Risk Rating | |||||||||
| Delivering, unloading and storing of PVC Pipe and fittings using pickup and unloading by manual handling | Plant and Traffic movement Run over by vehicles/plants Hit by reversing equipment Overhead obstructions Vehicle break down Property damage Collision with other vehicles Personal injury Fatality Accident due to poor lighting and visibility (operation at night | Operatives Staff/visitors | 3 | 4 | 12 | Medium | Delivery/ collection drivers shall be subject to induction/Training with regards to traffic management. Ensure exclusion zone is set up around the preparation work area and all plant movement and checked by supervisor Always use the pedestrian access provided Traffic light batons shall be provided for banks man at night All plant to have a fully trained banks man present all times. No plant to reverse without banks man. Ensure access route are sufficient and safe to use. Do not take rest in or under vehicles Proper barricade and safety signboard provided on open excavation All vehicles must be fitted with reverse alarm / Flashing light. The work place and all access to be well illuminated. Enforce Speed limit Ensure all vehicles entering the site is properly maintained and reported if found any defect Ensure materials are secured/tied in pallet trolley to avoid fall from trolley. | 1 | 4 | 4 | Low | Site Engr. Supervisor, Foreman, | ||||
| Manual Handling | Musculoskeletal disorders Hand injuries Cut & bruises | Operatives involved in work | 3 | 4 | 12 | Medium | Eliminate the need for manual handling by using mechanical aid. Reduce the weight of a load to limit force exertion If unsure of the load weight, check with supervisor. Ensure proper manual handling procedure Ensure adherence with sufficient and appropriate PPE. Limit load carrying to 20kg per person Supervisor must make sure while manual handling load individual task and environment to be considered to reduce the risk of manual handling. | 1 | 4 | 4 | Low | Supervisor, Foreman, Site Engr. | ||||
| Material storing | Slips, Trips and fall Poor house keeping | Operatives Staff / storekeeper | 3 | 4 | 12 | Medium | Ensure accesses are kept clear at all times. Housekeeping to be carried out regularly throughout the day when required Supervisor to ensure operatives are stacking material neatly and stacks are stable and in a safe condition Provide adequate lighting especially during night hours Appropriate space is allowed around storage areas for employees to move around safely without the risk being trapped between stacked materials. Maintain good housekeeping. | 1 | 4 | 4 | Low | Supervisor Foreman Site Engr. | ||||
| Installation of drainage Pipe (PVC) with accessories fittings using mobile Tower |
Work at height Fall form height Falling objects Over loading Protruding objects Access & egress | Operatives/ Staff/ Visitors Others | 3 | 4 | 12 | Medium | STARRT card briefing must before start the activity Ensure the PTW in place. Ensure proper working platform with complete fall protection Ensure Full body harness and 100% Tie off Ensure the scaffold platform is properly erected with “Safe to use” tag. Ensure castor wheels are locked Hand tools must be secured/tethered Work materials strictly not allowed to be stored on platform except for working tools Ensure avoid over reaching and climb on handrail. Ensure unauthorized person not allowed to modify the scaffolding and if needed to any changes then must be modified by trained and certified scaffolder. Ensure safe access to the working platform Scaffold access must be free from obstruction Ensure sufficient illumination in work area Ensure while fittings the GI clamp and brackets operatives must safely use drill machine to avoid finger injury. Ensure that working near fragile surface special care of body and eye protection with necessary PPE. Must clean the debris after completion the job and maintain good housekeeping. | 1 | 4 | 4 | Low | Supervisors Foreman Site Engineer | ||||
| Use of Ladder | Falling from height Working on Uneven ground Falling objects | Operatives/ Staff/ | 3 | 4 | 12 | Medium | Only light work, off short duration and work in which the operative can maintain secure hand and foot hold can be undertaken form a ladder Never try to overreach with any ladders Check the ladder is of suitable quality for industrial use and is in good condition Maintain a minimum of 3 points of contact with stepladders at all times (feet/thighs/hands) If possible avoid the use of stepladders at a working height of 2 meters and more. Check the ladder legs (and stays) are fully deployed or locked (depending on type) to maintain maximum base dimensions and the step ladder is orientated to provide maximum stability. Stepladders/ladders has to be used on leveled ground/firm base Ensure that during using ladder from the top 2 step is blocked to avoid climb on that. The ladder securely fixed to prevent slipping outwards or sideways or securely footed at all times. Person must hold the ladder while another operative working on it Materials should not be placed above the thread of ladders/step ladders | 1 | 4 | 4 | Low | Supervisor Site Engineer Foreman | ||||
| Do not carry any materials in one hand while climbing or getting down from ladder Ensure the area under the ladder is barricaded especially if it is being used in a public area. Ensure the ladder is electrical insulated podium type if working in live services | ||||||||||||||||
| Use of Glue Solvent, (Hazardous Substance) | Spillage/ soil contamination Burns Contact with skin Acute/Chronic adverse heath effect. Fire | Operatives using solvent | 3 | 4 | 12 | Medium | Ensure that all chemical substances have a COSHH assessment Refer SDS prior to any handling of hazardous substances and ensure SDS is easily accessible at site while working with chemicals. Ensure chemicals are properly stacked. Ensure all chemical containers are properly labeled. Spill kits to be available at site. Ensure operatives use the correct PPE Competent person to oversee the storage, use and disposal of hazardous materials. Ensure that correct welfare/first aid facilities are available in the area i.e. washing facility/eye wash. Proper and adequate PPE to be used always Ensure all chemical containers are properly labeled. Adjust work schedules so that workers are not overexposed to a hazardous chemical. Wear respiratory protection Ensure proper and adequate PPE to be used always. Ensure smoking only in designated area Ensure appropriate Firefighting equipment’s are in place and easily accessible | 1 | 4 | 4 | Low | Supervisors Foreman Site Engineer | ||||
| Use of power tools such as Grinder/Cutter & Drill machine, | Damaged Sockets & cable insulation. Electrocution Electric shock Short circuit & Burns Trip/Fall Noise Hearing loss Vibration Dust | Operatives and staff | 3 | 4 | 12 | Medium | All portable electrical equipment must be PAT tested and color coded. Make sure the test dates are visible on the equipment. Ensure all disk shall be appropriate and expiry date is over. Ensure all power tools are in good condition and appropriately maintained PTW to be obtained, prior to commencing the task Damaged industrial sockets and power cables must be removed. Ensure the electrical cable is not damaged and has not been repaired with insulating tape or unsuitable connectors. Ensure cables from power tools shall be organized so as not to present a tripping hazard Only trained competent operatives to operate the power tools. Ensure proper and regular maintenance of equipment that takes account of noise Ensure proper hearing protection always. Make sure people use the right tool for the job and are trained to use it correctly Ensure defective tools that require maintenance is reported for repair or replacement. Instruct workers to keep their hands warm and dry, and to not grip a vibrating tool too tightly. Ensuring proper job rotation and limiting time operatives working with power tools and hand tools. Use dust mask Ensure proper earth leakage protection is provided. All power tools must be 110V to be ensured. | 1 | 4 | 4 | Low | Supervisor Foreman Site Engineer | ||||
| Working under High temperature Direct sun light Dusty High wind | Heat exhaustion. Heat stroke Dehydration Personal injuries due to high temperature Sunstroke & Tiredness | Workers | 4 | 4 | 16 | High | Arrange adequate drinking water and rest shelter Drink plenty of water with electrolyte If feel something unusual immediately inform supervisor and report to site clinic. Make shift to operate the routine work Do not allowed alone work Frequent breaks Proper supervision available Correct PPE must use Provide heat stress training Conduct tool box talk Proper signage for drinking water | 1 | 4 | 4 | Low | Site Engr. Supervisors Foreman | ||||
| Working at night time | Poor visibility due to darkness / poor illumination Lone worker | Operatives/staff | 3 | 4 | 12 | Medium | Ensure proper night work permit is obtained Proper lighting system should be in place Ensure proper Communication / Coordination and close supervision Industrial safe torches to be available for emergency situations High visibility Traffic Vest for personnel’s in night shift Avoid lone working and always ensure buddy system while working at night Employees to be trained and understand crises plan. | 1 | 4 | 4 | Low | Site Engr. Supervisor Foreman | ||||
| Pressure Testing | Hydro test High-pressure leak of water Failure of hydraulic test pump Electric shock Electrocution | All operatives involved in work | 4 | 4 | 16 | High | Risk assessment must brief to the operatives. Ensure permit obtained for pressure test. All pressure tests must be conducted with due regard for the safety of life and property. Precautions should be taken to see that people not directly engaged in the testing operations remain out of the test area during the test period. During pressure testing events, distinct warning signs, such as DANGER – HIGH PRESSURE TESTING IN PROGRESS must be posted at the test work area with exclusion zone. Check that all high points have a tap or vent to facilitate removal of air during filling and that these are all closed. Blank, plug or seal any open ends and close all valves at the limits of the test section of the piping. Start to fill the piping and then ‘walk’ the route of the piping under test, continuously visually checking for leaks and by listening for the sound of escaping air Release air from all the high points systematically through the system to completely fill it with water Check that the test gauge is functioning correctly has been calibrated and has the correct range of the test pump. Check that a suitable hose is available for draining the system Before attempting test, Supervisor will review the test specifications and procedures with the Test Inspector and any other relevant personnel to be certain that all equipment is adequate, and duties are organized and understood All the electric live service must be temporary isolate to avoid electric shock and electrocution STARRT talk must conduct by supervisor PPE must in use with face shield Ensure proper grounding and earthling. After completion of the pressure test, release the water and disconnect all the temporary connections and close both ends Exclusion zone must be removing and remove the danger signage after completion of pressure test. | 1 | 4 | 4 | Low | Site engineer Supervisor Foreman | ||||
| Use of Hand tools | Improper selection of hand tools. Damaged and Defective Hand tools. Hand injuries Pinch point Ergonomics Repetitive strain injury | Operatives/Staff | 3 | 3 | 9 | Medium | Hand tools should be visually inspected for defects, prior to use. Never use damaged, blunt or broken tools to avoid injury. Select right tools for right Job Ensure no Homemade or makeshift tools to be used at site Remove from service any tool that shows signs of damage or defect Ensure Hand tools are Stored in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. Ensure hands are not in direct line of fire while working with hand tools Ensure appropriate PPE at all times. | 1 | 3 | 3 | Low | Site engr. Supervisor Foreman | ||||



.jpeg)
No comments:
Post a Comment