HDPE PIPE SPECIFICATION NOTES
By Er. Banwari Lal (contact@erbanwarilal.com)
·
The maximum
allowable hydrostatic design stress (σ) of a pipe is obtained by applying the design
coefficient of 1.25 ( Min ) to the MRS(minimum required strength) value of the
material, taking into consideration the temperature at which the pipe is to be
designed for
·
This standard is
applicable for the water supplies with a maximum operating pressure of 2.0 MPa.
PN 20 is maximum Nominal Pressure ( Pressure Rating Pipe )
·
Pressure Rating :-
Pipes shall be classified by pressure rating ( PN ) corresponding to the
maximum permissible working pressure at new 27 °C, (old 30°c), as
follows:
Pressure Rating of pipe :-PN2, PN 2.5, PN 3, PN 3.2, PN 4,PN 5, PN 6,PN 8, PN
10, PN 12.5, PN 16 ,PN20, (12 type pressure rating available)
Maximum Permissible working pressure( Maximum
Allowable operating pressure) :-{ PN (Pressure Rating ) ÷ 10 } MPa = 0.25MPa, 0.4MPa, 0.6MPa,1MPa,1.25MPa, 1.6MPa
(1MPa= 1N/mm2=10.197kg/cm2=10lakh Pascal’s
Pa)
·
The pipes are
recommended for maximum water temperature of +45 °C , The pip may also be used Up to the ambient
temperature of – 40 °C . As the creep rupture strength of the pipe varies
with the change in water temperature. the maximum working pressure, therefore,
should be modified by applying the pressure coefficient
·
Material Grade :-
PE 63 ,PE 80 , PE 100 (3 Category pipe material Grade)
·
MRS(Minimum
Required Strength) of Material in MPa,
at 20 °C for 50 Years is = Pipe Grade / 10 = PE63/10 = 6.3MPa
·
Maximum allowable hydrostatic design stress
(σ) for 20°C= MRS (Minimum Required
Strength) /design coefficient of 1.25
for 20°C for example PE 63 6.3(MRS)/1.25
=5MPa
·
Maximum allowable hydrostatic design stress
(σ) for 30°C= Value of 20°C Maximum Allowable hydrostatic design stress /design
coefficient of 1.25 for 20°C for example
PE 63 6.3(MRS)/1.25 =5MPa
For 30 °C = 5MPa/1.25= 4MPa
·
Standard Dimensions
Ratio ( SDR) = Nominal Out side diameter ,( Dn ) ÷ it’s nominal wall thickness (
En)
·
SDR cover in this
standard – SDR 41, 33 , 26 , 21, 17, 13.6 , 11, 9, 7.4 , 6
·
Nominal Diameter ( DN ) pipes covered in this standard
:- 16, 20, 25,32,40, 50,63,75,90, 110, 125,140, 160,180,200,225,250,280,315,355,400,
450, 500, 560 ,630, 710, 800,900 ,1000, 1200, 1400,
1600, 1800, 2000mm
·
The colour of the
pipe shall be black.
·
Each pipe shall
contain minimum three equispaced longitudinal stripes of width 3 mm ( Min ) in blue colour. Not be more than
0.2 mm in depth.
·
Pipes should not
constitute toxic hazard, should not support microbial growth and should not
give rise to unpleasant taste or odour, cloudiness or discoloration of water. Pipe
manufacturers shall obtain a certificate.
·
PE63(pipe
material Grade) available in all pressure rating that PN2.5, 4, 6, 10, 12.5,
and PN16
·
PE 80 available
in this pressure rating PN6 , PN10, 12.5, and PN16
·
PE100 available
in this pressure rating PN10, 12.5 and PN16
·
The outside
diameter shall be measured at a distance of at least 300 mm from the end of the
pipe. In the case of dispute, the dimension of pipes shall be measured after
conditioning at room temperature for 4 hours.
·
The length of
straight pipe shall be 5 m to 20 m
·
The pipes
supplied in coils shall be coiled drums of Minimum diameter of 18 times the
nominal diameter of the pipe ensuring that kinking of pipe is prevented.
·
The internal and
external surfaces of the pipes shall be Smooth, clean and free from grooving
and other defect
HDPE PIPE LAYING METHODOLOGY
Notes by Er. Banwari Lal contact@erbanwarilal.com
• SCOPE :- Methods of laying, jointing and testing of polyethylene (PE) pipes for the potable water supplies
• PE pipe is standard for water supplies up to and including 45°C water temperatures.
• PE pipe are UV protected (due to carbon black content in the pipe), may be stored either in open or covered.
• JOINTING TECHNIQUES :- A - Fusion welding (1. Butt fusion welding,2. Socket fusion welding,3. Electro fusion welding)
B- Insert type joints;
C- Compression fittings/push fit joints
D- Flanged joints
E- Spigot and socket joints
Note :- In this Methodology I covered only Fusion welding because of this is currently in practice of JJM/WRD related Maximum projects.
• The principle of fusion welding is to heat the two pipe surfaces to a designated temperature and then fuse them together by application of sufficient force. This force causes the melted materials to flow and mix, there by resulting in fusion.
• The site conditions must be protected against bad weather influences such as moisture and temperatures below 5°C.
• PE pipe has melt flow rate (MFR) range of 0.1–1.2 g/10 min at 190°C with nominal load of 5 kgf.
• Butt fusion equipment :- Basic welding machine shall be self-supporting such as guides and clamps to suit the stability of the basic machine,
A . Non-stick coated with poly tetra flouroethylene (PTFE), heating plate with thermostat and temperature indicator,
B. Chamfering ( Planing) tool — electrical/manual as appropriate (for square cut the pipe end)
C. Electro-hydraulic power pack (for sizes greater than 125 mm) unit with pressure indicator, by-pass arrangement and accumulator.
• Butt welding machines can be manual (for diameters up to 125 mm), hydraulic or pneumatic but equipment shall be locking system for protected against exerting over-pressure on the pipe. It shall be able to maintain the required interface force on the pipe or fittings end as long as necessary.
• PE pipe/fittings shall be jointing Same grade material and same pressure rating means if PE 80 Grade material pipe with PN6 pressure rating then this shall be join with same grade and pressure rating pipe /fittings,
• Procedure:-
A- Clamp the pipes/fitting in the butt fusion
machine.
B- wipe/clean the ends to be welded,
C- By planner ( pipe diameters greater than 160 mm) PE pipe / Fittings’ ends can be re-cut square.
D- Re-clean the surface with proper solvent.
E - Bring together the two ends and ensure they are aligned,
F - Check the hot plate (mirror) temperature (range 200-230°C) and make certain the plate surfaces are clean, ( The word ‘mirror’ has come into vogue because the heating plate radiates heat.)
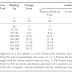
G- Move the pipe/fitting ends into contact with hot plate and a steady pressure of 0.15 ± 0.01 MPa shall be applied while a uniform bead forms around the circumference of the both ends.
H- After the bead height is formed as per *Table* relieve the pressure but maintain contact pressure between the plate and the ends of the heated surfaces as per pressure build up time mentioned in *Table*
I - Push back the pipe/fitting ends away from the Mirror after the above operation,
J - Bring the molten ends together and follow the recommended pressure as per the requirement of the pipe/fitting wall thickness *Table*. This pressure should be applied by building up gradually to avoid squeezing out too much of the melt. Do not disturb the joint during the required cooling time.
K - Relax the pressure and carefully remove the clamps only after ensuring that cooling time has elapsed.
NOTE :- Inside or outside bead removal after the weld joint cools, shall have no affect on the weld performance.
• The pipeline shall be laid Inside the trench with a slack of up to 2 m/100 m ( means 2% ) of Pipe line.
• PE pipe/ fittings joints do not require external joint restraints or thrust block joint anchors.
• To Facilitate locating a buried PE pipe, metallic locating Tapes or copper wires can be placed alongside the pipe. Locating tapes/wires are placed slightly above the Crown of the above before the final back fill.
• PE pipes can be used with special installation Techniques such as horizontal directional drilling, pipe Bursting, micro tunnelling methods of trench less Technologies
• Trench width shall be Dia + 300mm
• Trench depth shall be Dia + 1000mm to 1200mm , cover shall be 1 to 1.2 metre from top of pipe
• Under national/state highways, a concrete/hume pipe shall be covered over the pipe,
• In case of mole-plough technique of pushing the coils of diameters 20-100 mm in am narrow trench the width of 300 mm is not mandatory
• While laying in rocky areas suitable sand bedding should be provided around the pipe and compacted.
• initial back fill up to 150 mm above the crown of the pipe should be compacted with screened excavated material free of sharp stones or objects or with fine sand where no such material is available.
• Wherever road crossing with heavy traffic is likely to be encountered — a concrete pipe encasing is recommended.
• where the trench bottom is unstable, excess water should be removed before laying the pipe.
• Precaution — Polyethylene pipes shall not be installed near hot water pipes or near any other heat sources
• Load on the buried Pipeline shall not be permitted unless the trench has Been filled to the height of at least 300 mm over the Top of the pipe. Filling shall be done in layers of 150 mm, with the first layer watered and compacted By stamping or by mechanical means.
• FIELD TESTING OF PIPELINE
• The pipeline to be tested shall be filled with water Slowly allowing for splurging the entrapped air. Air Valves at high points should be open to allow air to Escape while water is being filled. Before pressure is Applied, the pipeline section under test shall be Restrained against movement.
• The following procedure is recommended for PE pipe Testing:
a) Polyethylene pipelines shall be pressure tested At ambient temperature. After filling with Water the pipeline shall be left to stabilize For a period of 1 h.
b) Fusion joints may be covered during testing. Flanged joints shall be kept open for visual Inspection. The pipeline shall be filled with Water and pressure tested from the lowest Point.
c) During the test period, make-up water is Continuously added to maintain the pressure.
d) The test pressure shall be 1.5 times the rated Pressure of pipes or of the proposed maximum Design pressure of the section. Apply the Pressure by continuously pumping at a Constant rate.
e) Under no circumstance, air is to be used Instead of water for testing.
f) Tests should be performed on reasonable Lengths of pipelines. Long lengths more than 2 000 m may make leak detection more Difficult.
g) Acceptance criteria — If the pressure remains Steady (within 5 percent of the target value) For 1½ h, leakage is not indicated. Flanged Connections shall be visually inspected.
h) If the test is not complete because of leakage Or equipment failures, the test section shall Be depressurized and allowed to relax for at Least 8 h, before starting the next testing Sequence.
i) Testing outside the trench is to be avoided, as Pipe rupture may involve safety issues.
• When failure or damage occurs in a welded Joint, the original weld shall be removed entirely before Re-welding. No patch work is recommended.
• Freezing of water inside the PE pipes does not fracture It, as the pipe expands to allow the extra volume.
• In case supply pressure Greater than the pressure Rating of the polyethylene pipe being installed, Adequate pressure reduction devices shall be installed.
• Surge Pressure :- In case for velocities higher than 1.5 m/s a surge Check is necessary.
• Air Valves, sluice valves, reducer, tee, fittings etc.. as per requirement use at site .
Table



.jpeg)
No comments:
Post a Comment