CHARACTERISTICS OF GOOD BUILDING STONES
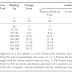
1. It should possess fine grained structure, uniform and pleasing colour. It should be free from soft patches, flaws and cracks.
2. The minimum strength of 3.5 N/mm2 is required for stone to be used for load bearing walls.
3. It should not absorb more than 5% water.
4. The specific gravity should not be less than 2.5.
5. In attrition test, it should not show wear of more than 2%.
6. Toughness index should be more than 10.
7. It should have good resistance to shocks and it should be durable.
Quarrying It is the process of extracting stones from rock bed, located near the earth’s surface and exposed to sun.
Quarrying may be done using hand tools, channeling machine or by blasting.
(a) Quarrying using hand tools: In soft rocks hand tools like chisels, hammers, pick axes and shovels may be used. Heating technique is suitable for getting aggregates. Wedging technique is suitable for quarrying in thin bedded rocks.
(b) Quarrying using channelling machine: This is suitable for large size quarrying in soft rocks like marble and limestone. Channels are 50 to 75 mm wide and 2.4 to 3.6 m deep. After channelling with machine wedges and drills are used to get stones.
(c) Quarrying by blasting: It consists of boring, charging, tamping and firing. The gas produced in the blast tries to come out by breaking the rock in all directions and succeeds in escaping along the Line of Least Resistance (LLR).
Dressing of stones The aim of preliminary dressing is to bring the size of stone approximately to the required size and reduce the transportation cost to great extent. Final dressing is as per the requirement of the user. The different methods of final dressing are:
(1) Hammer face; (2) Chisel drafted face; (3) Polished face and (4) Tooled finish.
Seasoning of stones The process of removing sap from the pores is known as seasoning. The best
method of seasoning is to allow the stones to dry for a period of 6 to 12 months in a shed.
Preservation of stones The following preservatives are used:
(1) Linseed oil; (2) Solution of alum and soap; (3) Solution of barium hydroxide; (4) Coal tar; (5) Paint and (6) Paraffin.



.jpeg)
No comments:
Post a Comment