What Is Estimation and Costing
What Is Estimation and Costing in The Civil Engineering
What is The Estimated Cost ?
All Civil and QC Engineering works or Construction works require the knowledge of probable cost of construction and beforehand, which is known as the estimated cost. If in any condition the estimated cost turns out to be the greater than the funds / money available then attempts are made to reduce the cost. This can be done either by changing the specificationss of the work or by reducing the work itself.
Accuracy in estimation is prime importance because if the estimate is exceeded it becomes very problematic for the Civil Engineers to account for and arrange the additional money. Inaccuracy in estimate can happen due to omission of items, improper rates, changes in design, calculations mistakes etc. For making accurate estimates one should be proficient in finding out the specifications and dimensions from the plan, Elevations and sections of the drawings.

Process of The Estimation in Constructions
Estimate is the basically the probable cost of a work. The estimate is calculated, before the commen cement of the constructions process, in order to derive or obtain the probable cost of any structure.
Learn More
How to calculate the number of bricks in 1 CFT wall
Estimations of any Constructions Project is Prepared by
1) . Calculating the quantities of materials required for the constructions
2) . Calculating the total cost by multiplying the quantities with suitable rates.
This way one gets the total expenditure likely to be incurred in the construction of the work/ building. The estimate should cover cost of materials, cost of labors, cost of transports, cost of scaffoldings, cost of equipments & machines, cost of the water, electricity, diesel, taxes, supervision cost, contractor cost and etc.
Learn More
What is The Actual Cost ?
After the completion of the work actual cost of the work can be assessed. On day 2 day basis an account of all the expenditure is maintained. These accounts are kept during the execution of work and after the work is completed final expenditure is calculated which is gives the actual cost. However, it should be taken care that the estimated cost & the actual cost should not differ from each other.
What is The Abstract or Estimated Cost ?
The cost of each item of the work is calculated from the quantities computed at the workable rates. This way is the total cost is worked out in the prescribed form. It is to be noted that a percentage of three to five percent is added to the contingencies. This is done to allow for the small contingent expenditures, future expenditures which are unforeseen, changes in design or fluctuations in the rates of the materials, labors, machinery and etc. in the markets, which may occur during the execution of the work.
Learn More
Also, a percentage of 1.5 to two percent is added to meet the expenditure requirements of the work charged establishment. The final total amount thus obtained is called the estimated cost of work.
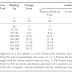
Item Number | Quantity | Units | Rates | Amounts |
Main Items of The Work in Estimation
1. Earthwork ( Estimation & Costing )
The earthwork is calculated in the cubic meters units. There are 2 separate types of earthworks first, the earthwork in excavations and second, the earthwork in fillings. By calculating the exact width of the foundations, the foundations trenches are dug out with vertical sides. Correct dimension of length, breadth and height of each foundation trench is taken and then the earthwork is calculated. Usually the filling of trenches after the constructions is not taken care of hence it is neglected.
Learn More
Types of Stone Masonry
The Construction Risk Management Guide
However in the case trench filling is accounted, it is computed by deducting the masonry from excavation. In plinth level filling, the earthwork is calculated by taking out the dimensions (length x breadth) in between plinth walls, which are usually less than the internal dimensions of the room by 2 offsets of plinth wall i.e., ten cm and height is taken by deducting the thickness of the concrete in floor, usually 7.5 cm.
Learn More
Building Estimation of Long Wall Short Wall And Center Line Method.
The earth which is excavated out is utilized in filling of the trenches and plinth filling. This is usually not paid for separately. This may be included as a separate item namely ‘Return fill and ram or backfills”. This is paid at lesser rates. If extra earth is required for the filling, it may be brought from outside. The excess earth left after the completion of trench filling and plinth filling is utilized for leveling and dressing. If not used the excess earth is removed from the site.
2. Concrete in Foundation ( Estimation & Costing )
The depth or thickness of the foundations concrete differs, however the length and breadth is usually the same. The concrete is usually calculated in the units cubic meters. The thickness of the concrete usually varies in the range 20cm-45cm and on an average 30 cm is taken. Foundation concrete is the mainly composed of lime concrete or weak cement concrete. Usually the proportions 1:4:8 or 1:5: 10 are taken of the cement concrete used in foundations.
3. Soling ( Estimation & Costing )
The practice of applying one layer of dry brick or stone below the foundations concrete, when the soil is soft or bad, is known as solings. The soling layers is calculated in the units square meter (length x breadth). The thickness is also specified.
Learn More
What Is Difference Between Pre-tension And Post-tension
4. Damp Proof Course ( Estimation & Costing )
Generally the D.P.C of 2.5 cm (1”) thick rich cement concrete 1:1.5:3 or 2cm (0.75”) thick rich cement mortar 1:2 , mixed with standard waterproofing material, is provided at the plinth level to the complete width of the plinth wall and the quantities are computed in square meter, (length x breadth). Deductions are made in the sills of doors and verandah openings because there no DPC is applied.
5. Masonry ( Estimations & Costing )
The computation of masonry is done in cubic meters (length x breadth x height). Masonry is dealt as 2 separate items- first – foundations and plinth masonry and second- masonry in superstructures. For a multi story buildings the masonry is computed separately for the each storey like the ground floor above plinth level, first floor, second floor and etc. In masonry the walls are measured as solid in taking out the quantities. After that deductions are made for doors, windows and etc (openings)
Different types or classes of masonry and masonry with the different mortar are taken under separate items. Arch masonry work is taken as a separate item. In arch masonry, the splayed or rounded sides of walls are considered as rectangular and extreme dimensions are taken to find out the requireds quantities. The partition walls which are thin are calculated in the square meters. In case of honey comb walls, it is dealt as a separate item and it is calculated in square meters. Suitable deductions are made for the holes also. The calculations done for the stone masonry is same as that made in the brick masonry.
Data for Estimation (Estimation & Costing)
The primary objective of any estimations is to make one know beforehand the cost of the work / projects. Actual cost of any work is only found after the completion of the work by checking the accounts of the expenditures. Hence , it becomes very important to prepare the estimates carefully and correctly so that there will not be a significant difference between the actual cost and the estimated cost. The estimator is required to be well experienced and fully acquainted with the methods of estimations.
For making an estimate for any Constructions work one needs the following data items, namely
- Drawings ( Plans, Section and etc )
- Specifications
- Rates
1. Drawings
For any Construction Projects, drawings are very important. Detailed drawings, fully dimensional and drawn to scale are needed. Plans, sectional elevations are required in the order to understand what is to be constructed. The plan, elevations and sectional elevations are drawn to a scale usually 1cm=1m(1”=8’). The detailed drawings are drawn to the scale 1cm=10cm to 1cm=29cm (1”=1 to 1”=2’).
Learn More
How Many Types Of Septic Tanks Based On Materials
How To Estimate Per Meter Weight Of Reinforcing Steel Bar
How To Calculate The Cutting Length Of Circular Stirrup
2. Specifications
Specifications are of mainly two types, namely
A) General specifications or brief specifications
B) Detailed specifications
A) General Specifications or Brief Specifications
These types of the specifications give a general view regarding the nature, quality and class of the work and materials to be used in the various tasks of the work. The general specifications is help to form a general idea of the whole building or the structure. The general specifications are also helpful in making the detailed specifications.
B) Detailed Specifications
These types of the specifications dives the detailed description number of tasks in the work such as laying down the quantities and qualities of materials, measuring their proportions, method of preparation, workmanship and executions of the work. The very important property of the detailed estimations is to describe each and every item of the work completely, separately and in details. This specification is the very useful for the executions of different items of work
3. Rates
The rates of the following items must be known rates per units of various items of the work, rates per units of various materials to be used in the constructions, rates of wages of different categories of labors like skilled, unskilled (masons, carpenters, mazdoors, kaarigars, electricians, plumbers and etc.) should be known to prepare the estimated of the constructions project. Points such as the location of the work and the work site distances from the source of materials, cost of transportation etc. should be known. Rates can be preferably taken from the P.W.D Schedule of Rate book or the rates may be worked out be the analysis of rate methods.
Learn More
How Many Types Of Septic Tanks Based On Materials
How To Estimate Per Meter Weight Of Reinforcing Steel Bar
Thumb Rules For Civil Engineers In Building Construction
Bar Bending Schedule for RCC Beam In Full Detail



.jpeg)
No comments:
Post a Comment