FORMWORK OR SHUTTERING- METHOD STATEMENT
As per Wikipedia, a formwork is temporary or permanent molds into which concrete or similar materials are poured. In the context of concrete construction, the falsework supports the shuttering molds. Formwork forms the shape of any concrete structure and is an ever-evolving part of the construction Industry. As technology’s influence has an effect on every other field so is with formwork too. Lightweight, easy-to-use Aluminium formworks (MIVAN), table formwork is common in India too, yet conventional formwork cannot be replaced fully. This post covers the Method of conventional formwork construction.
1. Purpose
The purpose of this document is to detail the Procedure for installation of conventional formwork for RCC structures on site. This procedure applies to all concrete work of permanent structure except lean concrete to be used as structural fill and backfill. The documentation will apply to all Engineers, Workmen, QC personnel, and other concerned persons associated with the work.
2. Scope of work

This Procedure covers the applicable codes and standards, sequence of work to be followed for the formwork erection of different structural elements which includes but is not limited to columns, slabs, walls, staircase construction manpower requirements, tools, and equipment required for the proper execution of works, quality and safety control measures required to complete the work in compliance to the satisfaction.
The scope of work consists of:
- Storage and control of materials
- Setting out.
- Formwork installation for different structural elements.
- Risk assessment, Hazard identification and it control measures.
3. References & Standards
- Reference Drawings
- Project Specific specifications
- IS: 4990 – PLYWOOD FOR FORMWORK SPECIFICATION
- IS 456 – PLAIN AND REINFORCED CONCRETE – CODE OF PRACTICE
- IS 14687 – FALSEWORK FOR CONCRETE STRUCTURES GUIDELINES
- IS 2062 – HOT ROLLED MEDIUM AND HIGH TENSILE STRUCTURAL STEEL SPECIFICATION
- IS 1977 – LOW TENSILE STRUCTURAL STEELS – SPECIFICATION
- IS 8500 – STRUCTURAL STEEL SPECIFICATION (MICRO ALLOYED) LOW & HIGH STRENGTH
- IS 1161 – STEEL TUBES FOR STRUCTURAL PURPOSES
- CPWD SPECIFICATIONS Volume 1 & 2 – GOVERNMENT OF INDIA CENTRAL PUBLIC WORKS DEPARTMENT
- IS 4082 – STACKING AND STORAGE OF CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS AND COMPONENTS AT SITE – RECOMMENDATIONS
4. Resources – a) Materials

All shuttering materials for the first use in the project shall be new which complies with the requirements laid out in IS 4990 – Plywood for formwork. Plywood shall be preservative treated, of BWP grade with either plastic coating or film faced. The thickness shall not be less than 12 mm.
The plywood shall be smooth and the faces and back shall be free from harmful discoloration, pleats, overlaps and loose knots. The edges shall be of smooth uniform finish.
Partially seasoned softwood timber shall be used to avoid swelling or warping. Timber which may be used for making strong scaffolding, beams, columns, props and bracings shall conform to IS 883.
Steel sheet plates conforming to IS 2062 or IS 8500 or IS 1977 may use for MS formwork for round columns (wherever applicable) elevation features and form lining, rolled sections and tubes conforming to IS 2062 or IS 8500 or IS 1161 may be used for steel forming and bracings. Manufacturer specification and tolerance shall be strictly followed to get the maximum capacity of the formwork system.
MS Props, MS Channels, H-Frames, Cup-locks shall be used with bracing using MS tube and swivel coupler for any scaffolding or MS props. Other, equivalent may be allowed as specified/approved.
Yokes, shrinkages, bolting and other mechanical devices will be used for tightening and fastening of the Form/ Falsework.
Wherever Chamfers are required or mentioned in the drawing chamfer Fillets-Proprietary fillets made of PVC/wood as approved to be provided.
De- Shuttering oil shall be of approved brands or as specified in the contract/specification.
b) Material delivery and storage
Plywood arriving at the site shall be lifted, carried, and stacked carefully to avoid damages to the corners of surfaces. Plywood shall be stored in packs on a level, flat, and raised surface in a clean, dry, and covered place with free circulation of air.
The stacking arrangement is to be done to protect them from rain, dampness, and excessive temperature. The edges of a board in a pack shall be in a straight vertical line. The top of the stack shall be covered with a cover board and weighed down suitably
The plywood panels shall not be dragged particularly those with plastic coating or with suitable overlay, over one another as this would scratch the surface of the edges are dragged on faces or any extraneous matter like sand or small stone particles lie in between the surfaces.
c) Oiling The Surface
Concrete shuttering plywood is capable of being re-used many times. One of the methods for maintaining such longer life of plywood is by coating the surface with suitable mould oil which acts both as a parting agent and gives surface protection.
The mould oil for use in coating the plywood should have the following basic characteristics:
It shall be free from the dark and other suspended particles and shall be of light grey color. Some manufacturers supply the boards already shop coated with mould oil.
After 3-4 uses and also in cases when plywood has been stored for a long time, it should be re-coated with mould oil before the next use.
d). Drying Of Panels
The plywood for concrete shuttering work may be used repeatedly. However, if it has to be stored for a long time after one use, the panels should be dried by stacking in the free circulation of air and on suitable spacers before storage.
e), Manpower
Project Engineer, Site Engineers, Supervisors, Foremen, and helpers.
5. Safety Precautions
- Safety of the personnel and properties is to be given prime importance and all works to be carried out without causing any accidents or property damages.
- Plywood and other related materials shall be stacked properly near the place of work (Do not stack too large quantity near the work area thereby causing safety hazard).
- Height of the stack should not be more than one and half meter.
- Scaffolding to be braced adequately.
- Working space to be clear of rubbish, waste mortar etc so that easy access and cleanliness is ensured.
- Scaffolding to be checked for the load carrying capacity and ensure no overloading.
- Lifting, manual transporting of conventional formwork materials etc must be carried out by workers who are properly trained. Otherwise, this may cause serious injuries to workers.
- Throwing of debris from height strictly prohibited.
- Before commencement of block work in front of lift shaft safety permit should be taken.
- CT props to be fixed in front of lift shaft to tie the safety belt.
- Hard barricading to be cut only by gas cutting (If any anchored in concrete along the openings and edges of the building).
6. Responsibility
The Project Manager/Construction Manager shall be responsible for the overall implementation of this procedure.
7.Preconstruction requirements
- Approved Good for construction drawing with latest revision issued shall be available with the construction team
- Shop drawings: Shop drawings for formwork shall be approved, stamped for GFC by all the concerned parties for architectural floor plans,
8. Equipment and Tools
- Hammer
- Plumb Bob
- Spirit Level
- Straight Edge
- Measuring Tape
- Tube Level
- Try Square Usage Tools,
- Wooden saw.
- Equipment to enable safe working at height.
9. Work procedure;
- Construction procedures should be planned in advance to ensure the safety of personnel and equipment and the integrity of the finished structure.

9a Formwork for Columns
Concrete shuttering formers for columns, piers, walls and other vertical surfaces are usually made by fixing the plywood onto a backing framework. The framework normally is made with timber or iron sections. The timber frame members shall be joined end to end by butt joint or lap joint or mitred joint. And the shuttering plywood shall be screwed or nailed to the framework.
For easy assembly and dismantling the formworks shall be made as separate panels (shooks) that can be joined side by side by using suitable nuts and bolts spaced at suitable distances. (eg: A column formwork shall consist of four panels/shooks or frames one for each side)
Steel frameworks may be of angled iron or channel section suitably fabricated and braced to which shuttering plywood can be fixed either by nuts and bolts or by screws, the latter driven from the steel frame side.
The plywood is so fixed on to the timber or steel framework that it gives a flush surface on the inside. The four-side frames are assembled into box form by use of nuts and bolts at appropriate distances, where holes have been drilled earlier.
After the concrete is poured and kept for the prescribed time, the former can be disassembled by opening the nuts and bolts fixed on the sides and reassembled or refixed for the second use with the same nuts and bolts.
Remaining Sections
9b. Formwork for Walls
9c. Formwork for Slab
9d.Formwork for Beams
9e. Working guidelines
10. Inspections
11. Tolerance & Tolerance Limit in shuttering (IS: 14687-1999)
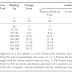
12. De-shuttering & De-Shuttering Criteria as per IS: 14687-1999
13. Verification Records
Download your Full copy

#FORMWORK #SHUTTERING #METHOD #STATEMENT



.jpeg)
No comments:
Post a Comment